Comprehensive Exploration of Automotive Wiring Harnesses
Automotive wiring harnesses are the backbone of automotive circuits, where contactor terminals (connectors) made of copper are combined with wires and cables to form a bundled circuit connecting assembly through the protection of plasticized and pressed insulators or metal housings.
This industrial chain covers a number of links such as wire and cable, connector manufacturing, processing equipment, wiring harness production and downstream applications, and its wide range of applications is not limited to automobiles, but also includes household appliances, computers and communications equipment and various types of electronic instruments.

The wiring harness of the car body is usually H-shaped, running through the entire body, to ensure the smooth connection of each electrical system.
It is worth mentioning that the automotive wires are made of copper multi-pistil soft wire, soft and not easy to break, and the hardness and thickness of household wires are significantly different. Household wires are usually copper single-piston, with a certain degree of hardness.
While the automotive wire is used in the copper multi-pistil soft wire, some of the soft wire is even as fine as a hair, by several to dozens of soft copper wire wrapped in plastic insulation tube, this design makes the automotive wire is both soft and not easy to break.
Design and Production Process of Automotive Wiring Harnesses
Comparison of European, American and Japanese Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process of automotive wiring harnesses in Europe and the United States, including China, is strictly controlled by the TS16949 system.
This system ensures that the manufacturing process is standardized, thus guaranteeing the quality and performance of automotive wiring harnesses.
In Japan, automakers such as Toyota and Honda have adopted a separate system to monitor the manufacturing process.
With the increasing functionality of automobiles, electronic control technologies are widely used, resulting in a proliferation of electrical components and wires, which in turn makes the wiring harnesses become thicker and heavier.
Modern automotive manufacturing has introduced CAN bus configurations that utilize an efficient multiplexing system, which significantly reduces the number of wires and interconnections and simplifies the wiring process as compared to traditional wiring harnesses.
Wiring Harness Specifications and Uses
The wires within automotive wiring harnesses come in a wide range of common specifications, including 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 4.0, 6.0, and other square millimeters of wire.
Different specifications of wires are suitable for different power devices, for example, 0.5 specification wire is commonly used in instrument lights, indicator lights and other low-power devices;
while 1.0 specification wire is suitable for turn signals, fog lights and other medium-power devices.
For main power wires, such as generator armature wires, hitch wires, etc., wires of 2.5 to 4 square millimeters are required.

Wiring Harness Diagrams and Wiring Fabrication
When arranging a wiring harness, a wiring harness diagram must be drawn in advance. A wiring harness diagram is different from a circuit schematic.
A wiring harness diagram is different from a circuit schematic diagram. The wiring harness diagram details how the electrical components are connected, and the wiring board is made according to the wiring harness diagram, which guides the workers in the assembly of the wiring harness.
Technicians at the wiring harness factory create a wiring harness layout board based on the wiring harness diagram, and then workers cut and route the wires according to the board.
The wiring harness of the entire vehicle is usually divided into several parts, including the engine (including ignition, EFI, power generation, and starter systems), instrumentation, lighting, air conditioning, and auxiliary electrical appliances, which include not only the main wiring harness, but also a large number of branch wiring harnesses.
Connection and Wrapping Materials for Wiring Harnesses
On the wiring harnesses, each end is printed with specific logo numbers and letters, and the connection between the wiring harnesses is made using coupling inserts, which are mostly wrapped with adhesive plastic tapes in modern times, and commonly used in the past for woven wires.
In addition, the wire is also divided into single-color wire and two-color wire, the use of its color has strict regulations, usually by the car manufacturers to develop their own standards.
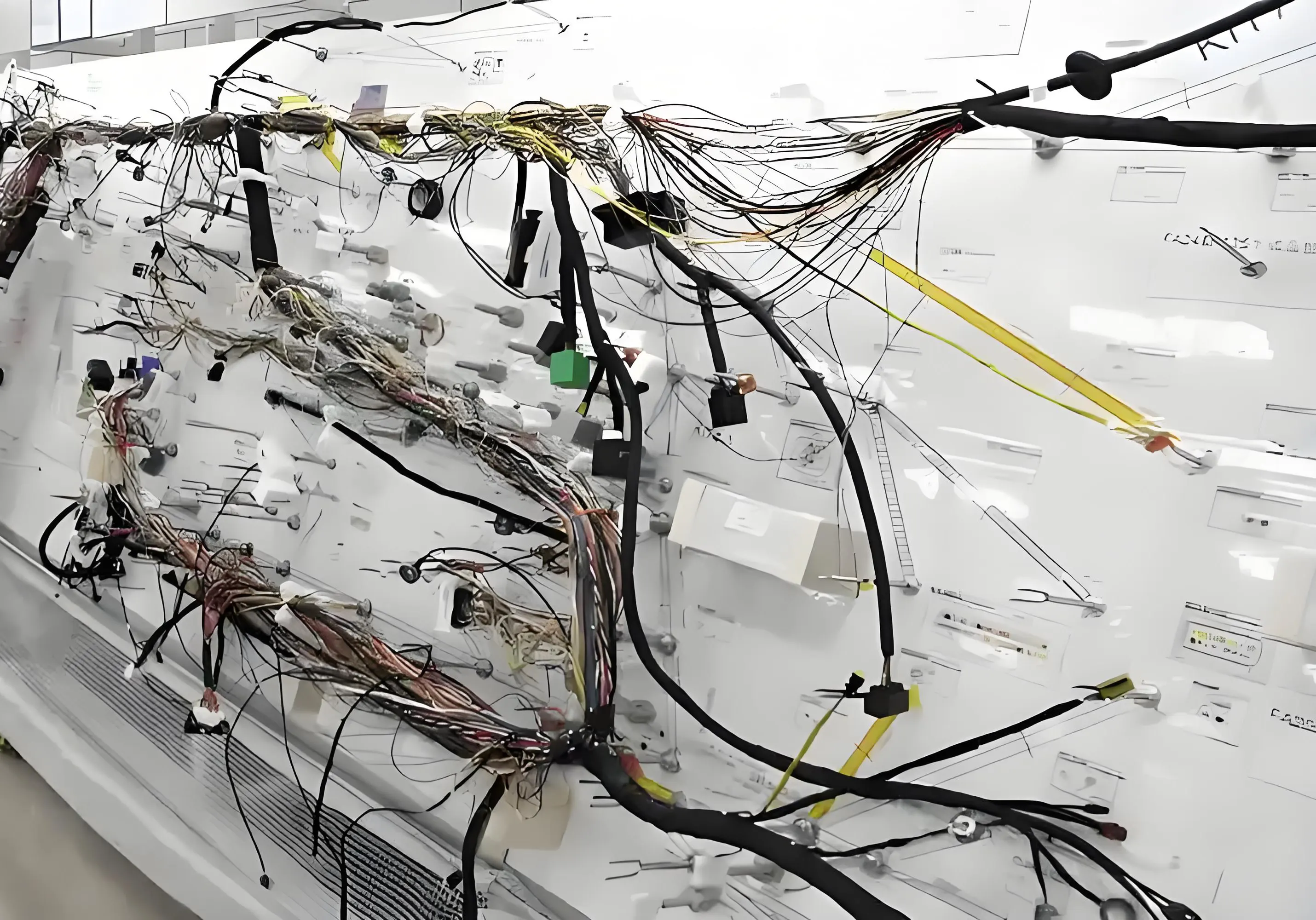

Material Selection Standards and Functions
Automotive wiring harnesses have extremely stringent requirements for materials, which not only require excellent electrical performance, but also need to have good material dispersion, temperature resistance and other characteristics.
Especially for the key components involved in vehicle safety, such as the direction control system and the brake system, the requirements are even more demanding. Wiring harness materials need to have good temperature resistance and material dispersion to prevent electromagnetic interference and eliminate the possibility of electrical short circuit.
In modern automobiles, there are a large number of automotive wiring harnesses, which are closely linked to the electronic control system.
Some people have used the human body as an analogy for the function of automobile components, in which the wiring harness is figuratively compared to nerves and blood vessels.
Automotive wiring harness as the core of the network of automotive circuits, responsible for connecting the electrical and electronic components and make them work properly.
Without wiring harnesses, automotive circuits cannot exist.
Recent Posts
2025-04-16 11:04:36
What is a wire-to-board connector?
2025-04-16 09:20:46
How to choose House Electrical Wiring?
2025-04-15 09:27:05


